With the rapid rise of IoT (Internet of Things) devices, connecting remotely to your gadgets has never been more crucial. Whether you're managing home automation systems, monitoring security cameras, or accessing smart appliances, understanding how to use remote IoT behind a router without MAC address restrictions is essential. This guide will walk you through the process step by step, ensuring you gain full control over your devices.
In today's interconnected world, IoT devices are revolutionizing the way we live and work. From smart thermostats to automated lighting systems, these devices offer convenience and efficiency. However, one common challenge many users face is accessing their IoT devices remotely, especially when their network has MAC address filtering enabled. This article will provide comprehensive solutions to overcome this issue.
By the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of how to configure your router settings, set up port forwarding, and utilize dynamic DNS services to ensure seamless remote access to your IoT devices. Let's dive in!
Read also:Discover The World Of Filmyfly Your Ultimate Movie Streaming Companion
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Remote IoT Access
- Understanding Router Basics
- What is MAC Address Filtering?
- Setting Up Port Forwarding
- Dynamic DNS for Remote Access
- Configuring Firewall Settings
- Useful Tools for Remote IoT Access
- Ensuring Security in Remote IoT Connections
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Remote IoT Access
Remote IoT access allows users to control and monitor their IoT devices from anywhere in the world. This capability is particularly valuable for individuals who manage smart homes, businesses that rely on IoT for operations, or hobbyists experimenting with connected devices. However, achieving this level of accessibility requires a solid understanding of network configurations and potential obstacles such as MAC address restrictions.
MAC address filtering is a security feature that limits network access to only those devices with approved MAC addresses. While this adds an extra layer of security, it can also hinder remote access if not properly configured. The following sections will explore methods to bypass these restrictions and ensure your IoT devices remain accessible from any location.
Understanding Router Basics
Types of Routers
Routers come in various types, each designed for specific purposes. For IoT devices, it's crucial to choose a router that supports advanced features like port forwarding, VLAN configurations, and guest networks. Here are some common router types:
- Wireless Routers: Ideal for home and small office environments.
- Enterprise Routers: Suitable for large-scale businesses with extensive network requirements.
- Mesh Routers: Provide seamless Wi-Fi coverage across large areas.
Router Settings Overview
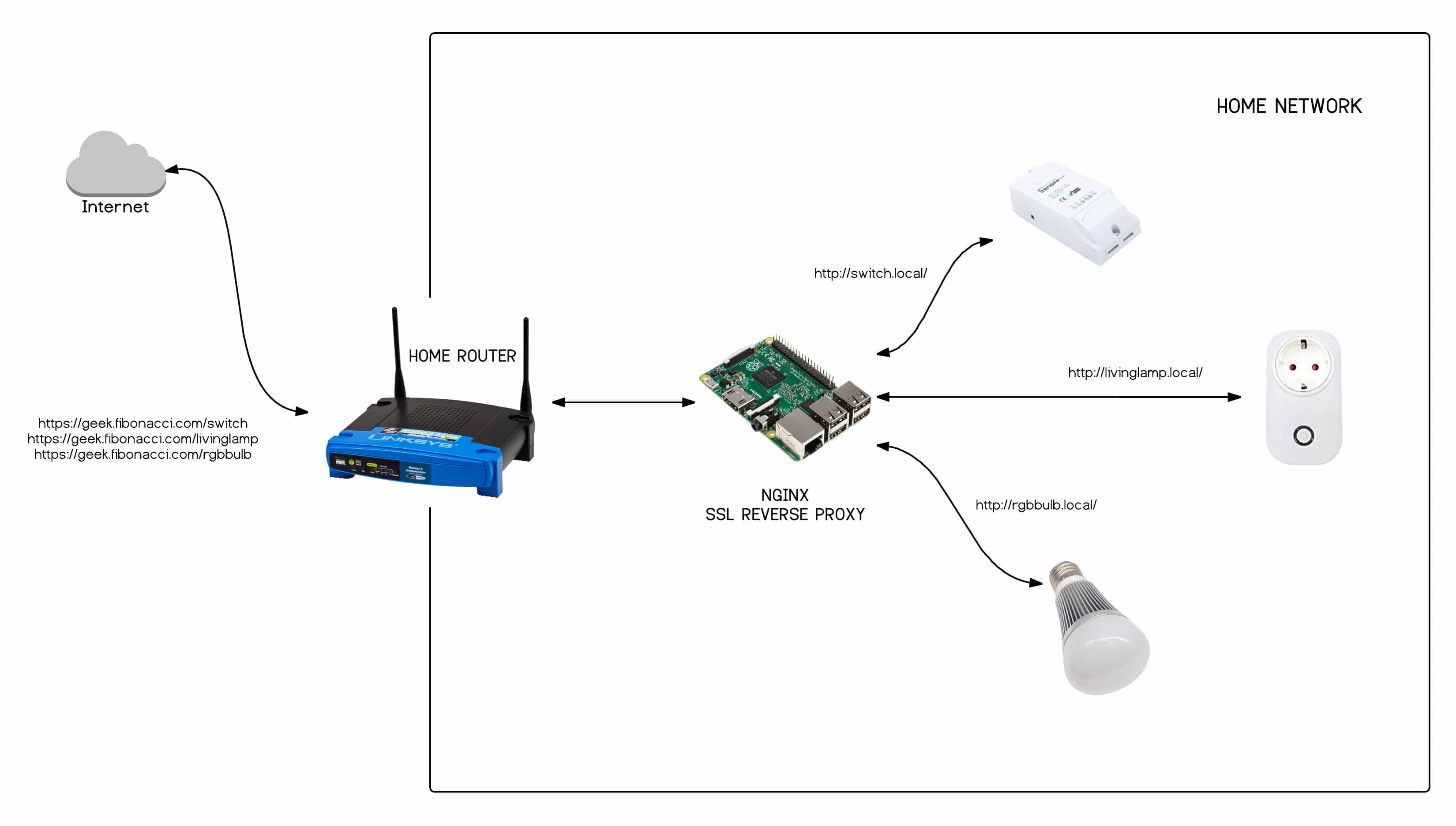
Accessing your router's settings typically involves logging into its web-based interface using an IP address such as 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1. Once logged in, you can modify settings related to Wi-Fi networks, security protocols, and advanced features like port forwarding and dynamic DNS.
What is MAC Address Filtering?
MAC address filtering is a security measure that restricts network access to devices with pre-approved MAC addresses. This feature can prevent unauthorized devices from connecting to your network but may also block legitimate devices if their MAC addresses aren't added to the whitelist.
To disable MAC address filtering, follow these steps:
Read also:Securely Connect Remoteiot P2p Ssh Hacker
- Log in to your router's web interface.
- Navigate to the Security or Wireless settings section.
- Locate the MAC Address Filtering option and disable it.
- Save the changes and restart your router.
Setting Up Port Forwarding
Why Port Forwarding Matters
Port forwarding allows specific ports on your router to be redirected to particular devices on your network. This is essential for remote IoT access, as it ensures incoming requests are directed to the correct device.
Steps to Configure Port Forwarding
Here's how to set up port forwarding:
- Access your router's web interface.
- Go to the Port Forwarding or NAT settings section.
- Add a new rule by specifying the external port, internal port, and IP address of the target device.
- Save the rule and test the connection.
Dynamic DNS for Remote Access
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) services map your router's dynamic IP address to a static domain name, making it easier to access your network remotely. Popular DDNS providers include No-IP, Dyn, and DuckDNS.
To set up DDNS:
- Sign up for a DDNS service and create a hostname.
- Configure your router to update the DDNS service with your current IP address.
- Test the DDNS setup by accessing your network using the assigned hostname.
Configuring Firewall Settings
Firewalls are essential for securing your network, but they can also block legitimate remote connections. To ensure smooth IoT access, you may need to adjust your firewall settings.
Adjusting Firewall Rules
Here's how to modify firewall settings:
- Access your router's firewall configuration page.
- Create an exception or rule that allows incoming traffic on the specified port.
- Save the changes and verify that the rule is active.
Useful Tools for Remote IoT Access
Several tools can simplify the process of remote IoT access:
- ngrok: A tunneling tool that creates secure tunnels for local servers.
- TeamViewer: A remote access software that supports IoT devices.
- SSH Tunneling: A method for securely accessing devices behind firewalls.
Ensuring Security in Remote IoT Connections
Security should always be a top priority when setting up remote IoT access. Here are some best practices:
- Use strong, unique passwords for all devices and accounts.
- Enable encryption protocols like WPA3 for Wi-Fi networks.
- Regularly update firmware and software to protect against vulnerabilities.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter problems while setting up remote IoT access, consider the following solutions:
- Verify that port forwarding rules are correctly configured.
- Check the status of your DDNS service and ensure it's updating properly.
- Test the connection using a different network or device to rule out local issues.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, accessing remote IoT devices behind a router without MAC address restrictions is achievable with the right configurations and tools. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure seamless connectivity while maintaining robust security measures.
We encourage you to share your experiences and insights in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site for more tips and tricks related to IoT and networking. Together, let's build a smarter, more connected world!
Data Source: Cisco IoT Overview