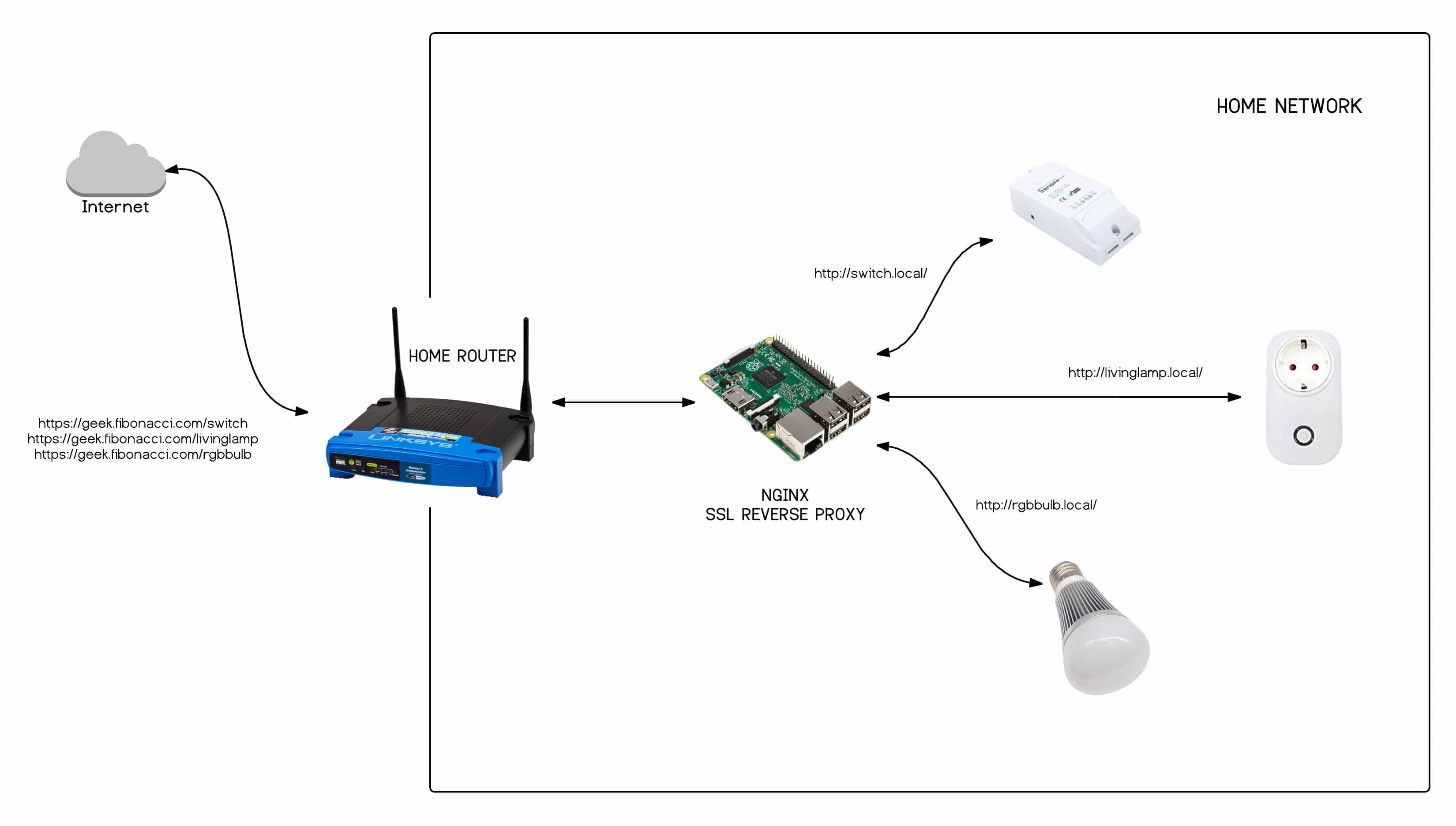
In today's interconnected world, the Internet of Things (IoT) plays a crucial role in enhancing our daily lives. From smart homes to industrial automation, IoT devices offer convenience, efficiency, and innovation. However, managing remote IoT devices behind a router can pose challenges, especially for those unfamiliar with networking concepts. This guide will walk you through how to use remote IoT behind a router while ensuring security and optimal performance.
As IoT adoption continues to grow, understanding how to configure and manage remote devices is essential. Whether you're a hobbyist, small business owner, or tech enthusiast, this article provides step-by-step instructions and practical tips to help you navigate the complexities of remote IoT management.
Additionally, we'll explore free download options for tools and software that simplify the process, ensuring you have the resources needed to succeed. Let's dive in and unlock the full potential of your IoT devices.
Read also:Securely Connect Remoteiot P2p Ssh Hacker
Table of Contents
- Introduction to IoT
- Understanding Routers and Networks
- Challenges of Remote IoT
- How to Configure Port Forwarding
- Securing Your IoT Devices
- Free Tools for Remote IoT
- Best Practices for Remote IoT
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Case Studies and Examples
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data over the internet. These devices range from simple sensors to complex machines, all designed to improve efficiency and automate processes. IoT has revolutionized industries such as healthcare, agriculture, and manufacturing, offering innovative solutions to everyday challenges.
Key Components of IoT
- Sensors: Devices that collect data from the environment.
- Connectivity: Methods of communication, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks.
- Cloud Computing: Platforms that store and process data.
- User Interface: Applications or dashboards that allow users to interact with IoT devices.
Understanding these components is crucial for effectively managing IoT devices, especially when accessing them remotely.
Understanding Routers and Networks
Routers are essential devices that manage network traffic and connect multiple devices to the internet. When IoT devices are connected to a local network, they are typically assigned private IP addresses, which are not directly accessible from the internet. To access these devices remotely, additional configuration is required.
Types of Networks
- Local Area Network (LAN): A network that connects devices within a limited area, such as a home or office.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): A network that spans a larger geographical area, connecting multiple LANs.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): A secure connection that allows remote access to a private network.
Understanding the differences between these networks is vital for configuring remote access to IoT devices.
Read also:Securely Connect Remote Iot P2p Raspberry Pi Free A Comprehensive Guide
Challenges of Remote IoT
Accessing IoT devices remotely presents several challenges, including security risks, network configurations, and performance issues. Without proper setup, unauthorized access or data breaches can occur, compromising sensitive information.
Common Challenges
- Firewall Restrictions: Many routers have firewalls that block unauthorized access to internal devices.
- Dynamic IP Addresses: Some internet service providers assign dynamic IP addresses, making it difficult to establish a stable connection.
- Bandwidth Limitations: Remote access can consume significant bandwidth, affecting overall network performance.
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning and implementation of best practices.
How to Configure Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is a technique that allows external devices to access specific ports on your local network. By configuring port forwarding, you can securely connect to IoT devices from anywhere in the world.
Steps to Configure Port Forwarding
- Log in to your router's admin interface using its IP address.
- Navigate to the "Port Forwarding" or "NAT" settings.
- Add a new rule, specifying the external port, internal IP address, and internal port.
- Save the changes and test the connection using a remote device.
For example, if your IoT device uses port 8080, you can forward this port to its internal IP address, enabling remote access.
Securing Your IoT Devices
Security is a top priority when managing IoT devices remotely. Implementing robust security measures ensures that your devices remain protected from potential threats.
Security Best Practices
- Change default passwords and use strong, unique credentials for each device.
- Enable encryption for data transmission, such as SSL or TLS.
- Regularly update firmware and software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Limit access to trusted devices and users using firewalls or access control lists.
By following these practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Free Tools for Remote IoT
Several free tools and software solutions are available to simplify remote IoT management. These tools offer features such as device monitoring, data visualization, and secure connections.
Recommended Tools
- PuTTY: A free SSH client for secure remote access.
- VNC Viewer: A remote desktop solution for controlling devices from a distance.
- OpenVPN: A free and open-source VPN solution for secure network access.
These tools can be downloaded and installed for free, providing valuable resources for managing IoT devices remotely.
Best Practices for Remote IoT
Adopting best practices ensures that your remote IoT setup is efficient, secure, and reliable. By following these guidelines, you can optimize performance and minimize potential issues.
Key Best Practices
- Document all network configurations and device settings for easy reference.
- Monitor network traffic and device performance regularly to identify potential issues.
- Implement redundancy measures, such as backup power supplies or network connections.
- Test remote access regularly to ensure stability and functionality.
These practices will help you maintain a robust and secure remote IoT environment.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Despite careful planning, issues may arise when managing remote IoT devices. Identifying and resolving these problems quickly is essential for maintaining uninterrupted service.
Common Issues and Solutions
- Connection Problems: Verify that port forwarding is correctly configured and that firewalls are not blocking access.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Optimize network settings and limit bandwidth usage for non-critical applications.
- Device Failures: Check device logs and firmware updates to diagnose and resolve issues.
By addressing these issues promptly, you can ensure that your IoT devices function as intended.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of remote IoT management. Companies across various industries have successfully implemented remote solutions to enhance productivity and reduce costs.
Example: Smart Agriculture
Agricultural businesses use remote IoT sensors to monitor soil moisture, temperature, and weather conditions. By accessing this data remotely, farmers can make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, leading to increased crop yields and reduced resource consumption.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, managing remote IoT devices behind a router requires a combination of technical knowledge, security measures, and best practices. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can configure and secure your IoT setup effectively, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
We encourage you to explore the free tools and resources mentioned in this article and apply them to your projects. Share your experiences and insights in the comments section below, and don't forget to check out our other articles for more valuable information.
Take Action Today! Start configuring your remote IoT setup and unlock the full potential of your devices.